The good news is that there is a proven and very simple rule of thumb to calculate the probabilities in the Texas Hold’em poker game: Outs x 2 + 1 = probability of improvement with one card. Outs x 4 = probability of improvement with the turn or river card.
In poker there are good bets and bad bets – the game is simply a way of determining who can tell the difference. This is where the concept of pot odds comes into play. Put simply, pot odds means is there enough in the pot to call a bet.
The fundamental principle of playing a drawing hand in poker is that you need a pot big enough to call. When we have a flush draw or a straight draw we will make our hand on the next card almost 20% of the time (19% for flush and 17% for the straight draw). That is, 20% of the time we will make our desired hand and 80% we won’t. The ratio 20 to 80 can be expressed as odds of 4-to-1. Therefore, if the pot is $80 we can almost call a $20 bet to break-even. I say almost because we have to make a profit so, a call of $20 is appropriate when there is more than $80 in the pot.
Know the Odds
You should already know how to calculate odds based upon the number of “outs”. If you don’t know the odds of hitting certain common draws then please go back and study our previous lesson on calculating odds and outs in poker. For the benefit of this lesson we’ll include the handy chart below:
Table: Odds and outs from the flop and the turn to the river:

We have created a printable PDF version of the poker drawing odds chart (opens in a new window). You will need Adobe Acrobat on your computer to view it on screen. We recommend you print the chart and be sure to memorize these odds, particularly the common draws – as your time is better spent analyzing your opponents’ play rather than attempting to perform mathematical calculations in your head.
Track the Pot Size
Part of the concept of pot odds is to focus on the calculation of how to figure the odds of your hand becoming a winner. The other part of the equation is to know how much is actually in the pot in order to know what odds it is offering you.
If you’re playing poker online then the size of the pot should be in clear view at all times – simple! If you’re playing poker live then it’s as easy as paying attention and using basic arithmetic to know the pot size at every step of the way. All one needs to do is multiply the total amount bet on each street by the number of active players and add that sum to the blinds if they are not participating in the hand. Hold that total in your head and add the subsequent total of the next street’s betting and you will always have the pot total available to calculate your pot odds. Here are some critical words of advice: know what is in the pot at all times. How else can you make proper mathematical decisions?
Calculating the Pot Odds
At this stage you should know the odds of hitting your card(s) and the size of the pot. The next step is to know what odds the pot is offering you. The best way to teach you is to use an example hand. Take a look at figure 1, below:
Figure 1
As you can see, we have 9 outs for the nut flush draw, so the odds of hitting our flush on the river are roughly 20% or 4-to-1 odds. There is $450 in the pot, and player 2 bets $150, which now makes the total pot $600. It’s going to cost us $150 to win $600. How do we calculate these figures to give us the pot odds? This is fairly simple as 600/150 = 4, so we have 4-to-1 odds for our money.
If we want to know the percentage then we add the bet (call amount) to the pot, to give us a total pot figure. In this example it would be: 150 + 600 = 750. Once we have this figure then we would have to perform the following formula: call amount / the total pot size. In our example this would be 150 / 750 = 0.2, or 20%.
Now we know the pot odds, should we call or not? In our example we can justify the call as we’re getting 4-to-1 pot odds and our odds of hitting and winning is also 4-to-1. But remember it’s a break-even call over the long term if we’re only counting the flush draw. Ideally we’d want the pot to be a little bigger or their bet to be a little smaller. However, if we believe that hitting either an Ace of King (giving us 6 additional outs) on the river would beat our opponent then we’d have more than enough odds to call the bet.
In poker, whenever the pot odds exceed the odds against making your hand, it pays to keep playing. When the odds against your hand coming in exceed the reward associated with it, it’s usually a bad deal. A simple way to think about this is as follows:
- When the prize exceeds the cost, you should call.
- If the cost is more than the money you figure to win, fold.
…did you know that AK flops a flush draw 11% of the time?
The new book Optimizing Ace King has a complete chapter on playing draws (along with chapters on playing pairs, turn & river play, and even ideal lines when AK totally misses the board).
As a bonus for being a Pokerology reader, use code POKEROLOGY at checkout to save $5 when you pick up your copy.
Let’s look at another example:
Figure 2
Here we have a straight and a flush draw, meaning we have 15 possible outs. The odds of hitting one of our outs on the turn is 31.9% or 2.13-to-1. The pot contains $36 ($24 + $12) and it’ll cost us $12 to call.
Are we getting enough pot odds to call? Let’s do the figures, first in odds…..$36 (total pot) / $12 (cost to call) = 3. Expressed as a ratio this would be 3-to-1 odds, meaning we’ll win once every 4 times. In percentage terms… the pot odds can be expressed as 25%. Our drawing odds are 31.9%. Since the pot is offering us better odds than our draw, we should call the $12 bet.
Let’s continue with this hand example. As you can see in figure 3, we didn’t hit on the turn, we check and our opponent then bets $60 into the existing $48 in the pot.
Figure 3
Are we still getting the correct pot odds to call in the hopes of hitting a straight or flush? The answer is no.
The pot odds are now 1.8-to-1 (108 / 60) or 35.7% in percentage terms. Our drawing odds are 2.07-to-1 or 32.6%. Since the pot odds are less than the odds of hitting, in this instance we should fold. To call a bet here we’d need the pot to be a little bigger or our opponents bet to be a little lower. He has priced us out with his overbet.
So, that old feeling we had, “There is a bunch of money in the pot, I call”, was and is a sound tactic. Now we know more precisely when it is profitable and when it is not profitable to go in on draws. Knowing pot odds does two things; it lets us concentrate on the other players and turns poker into a game of skill.
Make Your Opponents Pay
Let’s take a quick look at a situation when you’re the one with a made hand and you figure one or more of your opponents to be drawing. Understanding the concept of pot odds should help you to determine an appropriate bet size and charge your adversaries for their possible draws.
Imagine raising a bunch of limpers from late position, holding pocket Jacks. The big blind and the three of the original limpers all call your raise and the five of you watch a flop of :
You’ve hit middle set but there are both straight and flush draws staring at you along with four opponents. There is $86 in the pot and everyone checks to you. You are definitely going to make a continuation bet but you need to decide on how much. Allow me to provide a check list of criteria to think about that as you become more experienced will become so automatic as to not even require any conscious thought.
- Know the pot size – in this case $86.
- Acknowledge the texture of the flop and tendencies of your opponents in terms of potential threats to your holding. Limpers and callers are many times on draws.
- Know the odds to the potential draws the flop offers. In this case both flush and straight draws.
- Make a bet that will not offer the potential draws the correct odds.
- You should bet the size of the pot, $86, in order to make the odds being offered by the pot only 2-to-1 which would not be attractive odds for draws.
If it is true, and I believe it is, that the bulk of your poker profit comes from the mistakes of others rather than you own brilliant play, then identifying opponents that overpay to draw to their hands is critical information. Aside from just playing too many hands, one of the biggest and most expensive mistakes less experienced poker players commit is paying too high a price to try to make their draws. Ferret this information out by tracking the pot and watching showdowns and then you can determine how to manipulate the size of the pot against that opponent in a future hand.

Implied Odds
Turn River Poker
This is an extension of pot odds and represents the ratio of the total amount you expect to win if you complete your hand, to the amount you would need to call to continue. Put simply, you don’t have the correct odds to call, but if you reason that there’s a good chance that your opponent will bet again when you hit your draw, you might be getting the implied odds to call.
While implied odds are an important tool to be aware of, particularly in no limit hold’em, many less disciplined players abuse it by using it as a justification to chase draws that are not getting the proper pot odds. While pot odds can be calculated with total accuracy, calculating implied odds takes some guess work and knowledge of your opponents’ tendencies. It’s more of an art than a science.
Are your opponents mostly fish?
If yes, they tend to offer a lot of implied odds – but most players leave chips on the table by missing aggression AND using incorrect bet/raise sizes when they hit their hand.
To ensure you don’t fall into the same trap, sign up for CORE today and pay special attention to the lessons on:
Poker Odds Flush Turn River Poker
· Value Betting (Level 1)
· Overbetting (Level 2: Postflop)
· Range Elasticity (Level 2: Ranges)
Enroll today for just $5 and see how pot odds (along with 100+ other concepts) fit into the entirety of your poker playbook!
Poker Odds Flush Turn River Capital
Tournament Play
Much of what has been offered so far is beneficial for both cash games and poker tournaments. But you should approach opponents in tournaments that are desperate a little differently. In a cash game, being pot committed doesn’t really come into play. The term pot committed simply refers to a player who has half or more of his chips already in the pot so if he loses this pot he is pretty much finished anyway. This player will be calling, not based upon the pot odds, but due to his predicament. Players calling in tournament play without the correct pot odds does not necessarily indicate poor play. Calling may well still represent their best chance mathematically to move forward in the tournament and make some money. Hence the expression, do or die!
The reverse situation relative to pot odds can also occur in tournament play. Imagine being in a situation wherein you have the correct pot odds to call but folding could be the better option to advance. An example of this type of phenomenon would be holding the nut flush draw with one card to come with two other opponents already all-in by a monster stack late in a poker tournament. The pot could be offering you greater than the odds required to make the call mathematically correct but the fact still remains that you will miss your flush 80% of the time. If you were on the bubble with the big stack bully already having two other players all-in and you knew you would only prevail in the hand 20 percent of time – I think a fold would be in order.
Many believe that pot odds aren’t nearly as important in tournament play. This is especially true in the lower stake “fast” events that are typical in both live and internet play. These players focus on the odds of their opponents’ calling based upon the size of chip stacks. While some of this is true, if you begin to ignore pot odds because you are in a poker tournament, you will begin to slide down a slippery slope. If you are planning to make a decision that is not in accordance with good pot odds play, you should have a very significant reason.
Put in the Work
Knowing what and how to use pot odds is essential if you wish to become a winning poker player. Learning how to use these concepts to your advantage can put you well ahead of a vast legion of players that are just too lazy to put in the work. They are playing on feel and their gut instincts and proud of it. I’m happy they’re proud of this approach because I know they can’t be proud of their bankrolls. These “proud” players are the assets you need in both cash games and tournaments. Let them be proud – you should put in the work – you’ll be glad you did as you’ll end up with their bankrolls.
Related Lessons
By Tom 'TIME' Leonard
Tom has been writing about poker since 1994 and has played across the USA for over 40 years, playing every game in almost every card room in Atlantic City, California and Las Vegas.
Related Lessons
Related Lessons
The main underpinning of poker is math – it is essential. For every decision you make, while factors such as psychology have a part to play, math is the key element.
In this lesson we’re going to give an overview of probability and how it relates to poker. This will include the probability of being dealt certain hands and how often they’re likely to win. We’ll also cover how to calculating your odds and outs, in addition to introducing you to the concept of pot odds. And finally we’ll take a look at how an understanding of the math will help you to remain emotional stable at the poker table and why you should focus on decisions, not results.
What is Probability?
Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with the likelihood that one outcome or another will occur. For instance, a coin flip has two possible outcomes: heads or tails. The probability that a flipped coin will land heads is 50% (one outcome out of the two); the same goes for tails.
Probability and Cards
When dealing with a deck of cards the number of possible outcomes is clearly much greater than the coin example. Each poker deck has fifty-two cards, each designated by one of four suits (clubs, diamonds, hearts and spades) and one of thirteen ranks (the numbers two through ten, Jack, Queen, King, and Ace). Therefore, the odds of getting any Ace as your first card are 1 in 13 (7.7%), while the odds of getting any spade as your first card are 1 in 4 (25%).
Unlike coins, cards are said to have “memory”: every card dealt changes the makeup of the deck. For example, if you receive an Ace as your first card, only three other Aces are left among the remaining fifty-one cards. Therefore, the odds of receiving another Ace are 3 in 51 (5.9%), much less than the odds were before you received the first Ace.
Want to see how poker math intertwines with psychology and strategy to give you a MASSIVE EDGE at the tables? Check out CORE and learn poker in the quickest and most systematic way:
Pre-flop Probabilities: Pocket Pairs
In order to find the odds of getting dealt a pair of Aces, we multiply the probabilities of receiving each card:
(4/52) x (3/51) = (12/2652) = (1/221) ≈ 0.45%.
To put this in perspective, if you’re playing poker at your local casino and are dealt 30 hands per hour, you can expect to receive pocket Aces an average of once every 7.5 hours.
The odds of receiving any of the thirteen possible pocket pairs (twos up to Aces) is:
(13/221) = (1/17) ≈ 5.9%.
In contrast, you can expect to receive any pocket pair once every 35 minutes on average.
Pre-Flop Probabilities: Hand vs. Hand
Players don’t play poker in a vacuum; each player’s hand must measure up against his opponent’s, especially if a player goes all-in before the flop.
Here are some sample probabilities for most pre-flop situations:
Post-Flop Probabilities: Improving Your Hand
Now let’s look at the chances of certain events occurring when playing certain starting hands. The following table lists some interesting and valuable hold’em math:
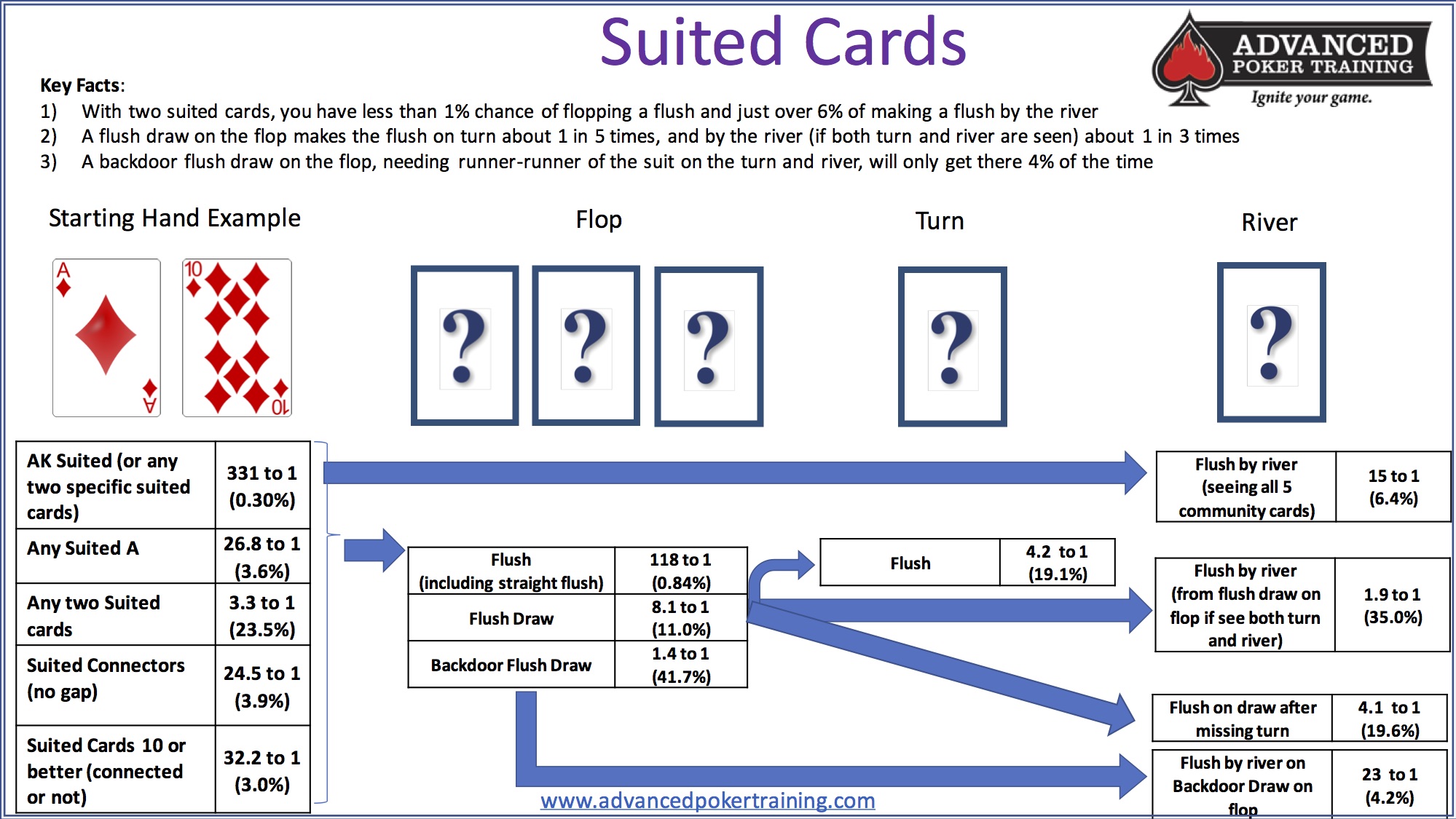
Many beginners to poker overvalue certain starting hands, such as suited cards. As you can see, suited cards don’t make flushes very often. Likewise, pairs only make a set on the flop 12% of the time, which is why small pairs are not always profitable.
PDF Chart
We have created a poker math and probability PDF chart (link opens in a new window) which lists a variety of probabilities and odds for many of the common events in Texas hold ‘em. This chart includes the two tables above in addition to various starting hand probabilities and common pre-flop match-ups. You’ll need to have Adobe Acrobat installed to be able to view the chart, but this is freely installed on most computers by default. We recommend you print the chart and use it as a source of reference.
Odds and Outs
If you do see a flop, you will also need to know what the odds are of either you or your opponent improving a hand. In poker terminology, an “out” is any card that will improve a player’s hand after the flop.
One common occurrence is when a player holds two suited cards and two cards of the same suit appear on the flop. The player has four cards to a flush and needs one of the remaining nine cards of that suit to complete the hand. In the case of a “four-flush”, the player has nine “outs” to make his flush.
Poker Odds Flush Turn River Green
A useful shortcut to calculating the odds of completing a hand from a number of outs is the “rule of four and two”. The player counts the number of cards that will improve his hand, and then multiplies that number by four to calculate his probability of catching that card on either the turn or the river. If the player misses his draw on the turn, he multiplies his outs by two to find his probability of filling his hand on the river.
In the example of the four-flush, the player’s probability of filling the flush is approximately 36% after the flop (9 outs x 4) and 18% after the turn (9 outs x 2).
Pot Odds
Another important concept in calculating odds and probabilities is pot odds. Pot odds are the proportion of the next bet in relation to the size of the pot.
For instance, if the pot is $90 and the player must call a $10 bet to continue playing the hand, he is getting 9 to 1 (90 to 10) pot odds. If he calls, the new pot is now $100 and his $10 call makes up 10% of the new pot.
Flush Poker Hand
Experienced players compare the pot odds to the odds of improving their hand. If the pot odds are higher than the odds of improving the hand, the expert player will call the bet; if not, the player will fold. This calculation ties into the concept of expected value, which we will explore in a later lesson.
Bad Beats
A “bad beat” happens when a player completes a hand that started out with a very low probability of success. Experts in probability understand the idea that, just because an event is highly unlikely, the low likelihood does not make it completely impossible.
A measure of a player’s experience and maturity is how he handles bad beats. In fact, many experienced poker players subscribe to the idea that bad beats are the reason that many inferior players stay in the game. Bad poker players often mistake their good fortune for skill and continue to make the same mistakes, which the more capable players use against them.
Decisions, Not Results
One of the most important reasons that novice players should understand how probability functions at the poker table is so that they can make the best decisions during a hand. While fluctuations in probability (luck) will happen from hand to hand, the best poker players understand that skill, discipline and patience are the keys to success at the tables.
A big part of strong decision making is understanding how often you should be betting, raising, and applying pressure.
The good news is that there is a simple system, with powerful shortcuts & rules, that you can begin using this week. Rooted in GTO, but simplified so that you can implement it at the tables, The One Percent gives you the ultimate gameplan.
This 7+ hour course gives you applicable rules for continuation betting, barreling, raising, and easy ratios so that you ALWAYS have the right number of bluffing combos. Take the guesswork out of your strategy, and begin playing like the top-1%.
Conclusion
A strong knowledge of poker math and probabilities will help you adjust your strategies and tactics during the game, as well as giving you reasonable expectations of potential outcomes and the emotional stability to keep playing intelligent, aggressive poker.
Remember that the foundation upon which to build an imposing knowledge of hold’em starts and ends with the math. I’ll end this lesson by simply saying…. the math is essential.
Related Lessons
By Gerald Hanks
Gerald Hanks is from Houston Texas, and has been playing poker since 2002. He has played cash games and no-limit hold’em tournaments at live venues all over the United States.
Comments are closed.